
ISO 9001: Guide to Quality Management & Certification
Learn about ISO 9001 standards, requirements, costs, and the steps to implement a Quality Management System (QMS) for your business.
ISO 9001: Your Guide to Quality Management
Every business leader wants to build a more efficient, customer-focused, and resilient organization. Achieving these goals requires more than just good intentions; it demands a structured approach to quality. This is where ISO 9001 comes in. As the globally recognized standard for Quality Management Systems (QMS), it provides a framework for organizations to consistently meet customer expectations and enhance satisfaction.
Achieving an ISO 9001 certification isn't just about earning a badge; it's a strategic commitment to excellence. It signals to your customers, partners, and employees that your organization is dedicated to continuous improvement and operational integrity. By implementing a robust QMS, you empower your team, streamline processes, and create a culture where quality is everyone’s responsibility.
This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about ISO 9001. We'll cover the standards, requirements, costs, and the step-by-step process of implementation. You'll learn about the tangible benefits, common challenges, and how to leverage tools and resources to make your certification journey a success.

Understanding ISO 9001: Standards and Requirements
ISO 9001 is the international standard that specifies requirements for a quality management system. Developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), it helps businesses and organizations be more efficient and improve customer satisfaction. The current version, ISO 9001:2015, is built upon seven key quality management principles:
- Customer Focus: Understanding and meeting customer needs and striving to exceed their expectations.
- Leadership: Establishing a unified direction and creating conditions in which people are engaged in achieving the organization's quality objectives.
- Engagement of People: Recognizing, empowering, and enhancing the competence of people at all levels to create and deliver value.
- Process Approach: Managing activities and related resources as interrelated processes that function as a coherent system.
- Improvement: Maintaining a constant focus on improvement.
- Evidence-Based Decision Making: Making decisions based on the analysis and evaluation of data and information.
- Relationship Management: Managing relationships with interested parties, such as suppliers, to sustain success.
The standard also emphasizes risk-based thinking, which involves identifying risks and opportunities proactively to prevent or reduce undesired effects and drive improvement.
Implementing Your Quality Management System (QMS)
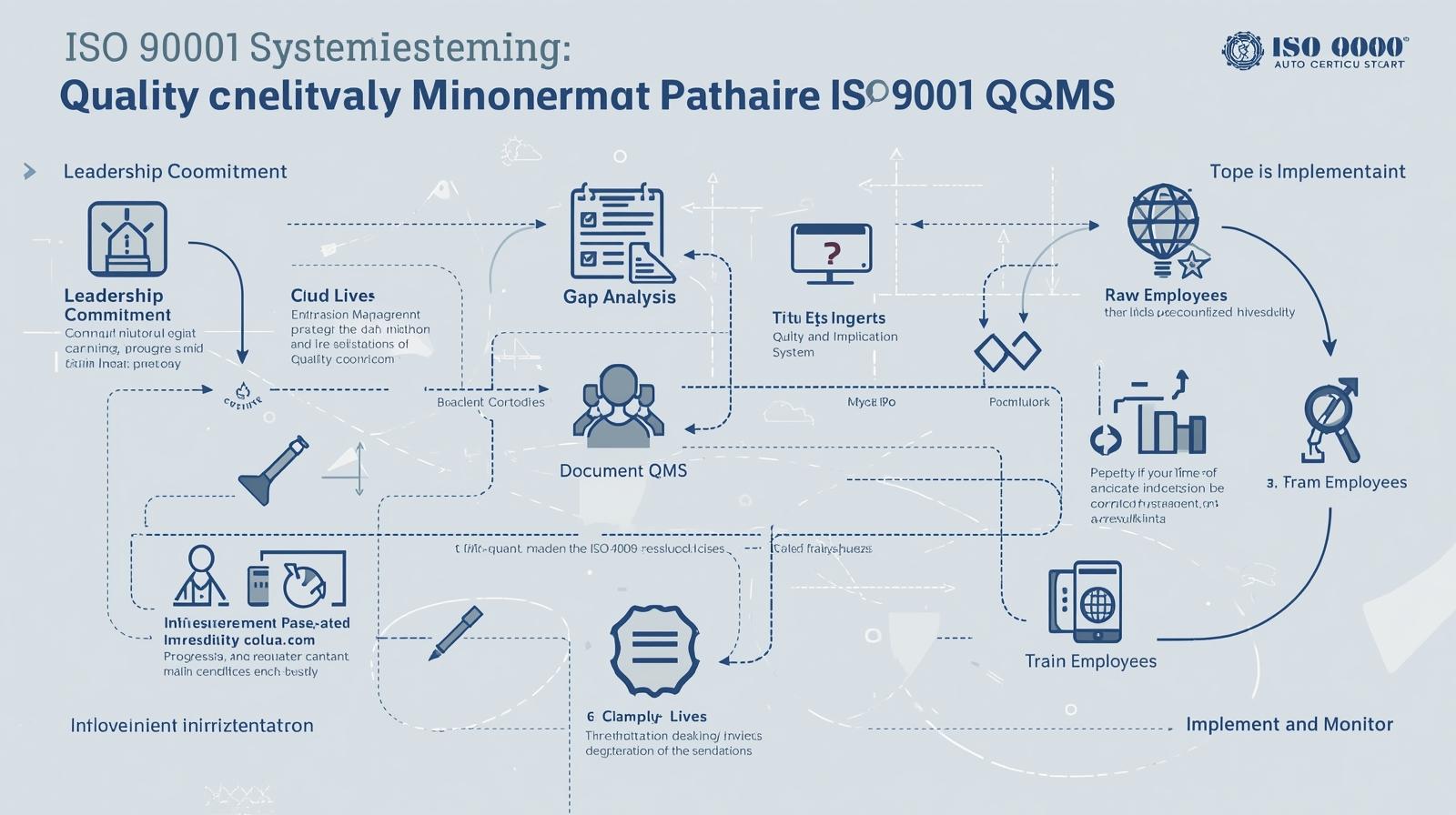
Achieving ISO 9001 certification requires a systematic approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide to implementing your QMS:
Step 1: Gain Leadership Commitment
Your ISO 9001 journey begins at the top. Senior management must understand and champion the importance of the QMS, allocating the necessary resources and fostering a culture of quality.
Step 2: Conduct a Gap Analysis
Evaluate your current processes against the ISO 9001:2015 requirements. This analysis will identify areas where your organization already complies and where improvements are needed.
Step 3: Plan Your Implementation
Develop a detailed project plan. Define the scope of your QMS, set clear objectives, establish timelines, and assign roles and responsibilities to your team.
Step 4: Document Your QMS
ISO 9001 requires specific documentation, including a quality policy, objectives, and information about your processes. Create clear, concise, and accessible documentation that reflects how your organization operates.
Step 5: Train Your Employees
Your team is central to the success of your QMS. Provide comprehensive training to ensure everyone understands their roles, responsibilities, and how their work contributes to the organization's quality objectives.
Step 6: Implement and Monitor the QMS
Put your documented processes into action. Continuously monitor performance, collect data, and track your progress against your quality objectives. This is where you bring your QMS to life.
Step 7: Conduct Internal Audits
Regular internal audits are crucial for verifying that your QMS is effective and compliant with ISO 9001 standards. Use these audits to identify non-conformities and areas for improvement.
Step 8: Undergo the Certification Audit
Once your QMS is fully implemented and you have conducted at least one full internal audit cycle, you can engage an accredited certification body. The audit is typically a two-stage process:
- Stage 1: A review of your documentation to ensure it meets ISO 9001 requirements.
- Stage 2: An on-site audit to verify that your processes are being followed in practice.
Upon successful completion, you will be awarded an ISO 9001 certificate.
The Costs of ISO 9001 Certification
The cost of achieving ISO 9001 certification varies depending on the size and complexity of your organization. Key expenses to consider include:
- Implementation Costs: This includes resources for gap analysis, documentation, and employee training. Using a platform like youable can help streamline these processes and manage costs effectively.
- Certification Body Fees: These are the fees charged by the accredited body for conducting the Stage 1 and Stage 2 audits.
- Ongoing Maintenance: After certification, you will have annual surveillance audits and a recertification audit every three years, which have associated costs.
While there is an initial investment, the long-term return on investment from improved efficiency, reduced waste, and increased customer satisfaction often far outweighs the costs.
Tangible Benefits of ISO 9001 Certification
Achieving ISO 9001 approval is a powerful strategic move that delivers significant benefits, transforming your organization from the inside out.
Improved Efficiency and Cost Savings
By standardizing processes and focusing on continuous improvement, organizations can significantly reduce waste and operational inefficiencies. For instance, a manufacturing company that implemented ISO 9001 reduced its defect rate by 40%, leading to substantial cost savings and higher product quality. Similarly, a construction company used the standard to reduce project delays and cost overruns.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
A core principle of ISO 9001 is a relentless focus on the customer. By systematically gathering and responding to feedback, organizations can better meet and exceed customer expectations. One service provider saw its customer satisfaction scores increase by 25% after adopting ISO 9001 principles to streamline its responsiveness.
Increased Credibility and Market Access
An ISO 9001 certification demonstrates a commitment to quality that can open doors to new markets and clients. Many government agencies and large corporations require their suppliers to be ISO 9000 certified. An IT company successfully secured a major government contract by showcasing its ISO 9001 certification as proof of its robust quality management processes.
Overcoming Common Implementation Challenges
The path to certification is not always smooth. Here are common hurdles and how to clear them:
- Resistance to Change: Engage employees early and communicate the "why" behind the changes. Highlight the benefits for them and the organization.
- Lack of Management Commitment: Present a clear business case to leadership, focusing on ROI, risk reduction, and competitive advantage.
- Inadequate Documentation: Use templates and tools like youable to simplify record-keeping and ensure compliance.
- Poor Training: Develop a targeted training program that is relevant to each employee's role within the new QMS.
- Integration Issues: Plan for the integration of your QMS with existing systems from the start to avoid creating data silos.
- Underestimating Resources: Create a realistic budget and timeline based on a thorough gap analysis.
The Future of Quality Management and ISO 9001
The world of quality management is evolving. Key future trends include:
- Digital Integration: Technologies like AI and blockchain will be used for advanced data analysis and process automation within the QMS.
- Sustainability Focus: Expect a greater emphasis on integrating environmental and social responsibility into quality management practices.
- Remote Auditing: The shift towards remote audits will continue, improving the efficiency and accessibility of the certification process.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: QMS will increasingly focus on customer experience as a primary driver of quality.
- Predictive Analytics: The use of predictive analytics will enable organizations to be more proactive in problem-solving and continuous improvement.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the purpose of ISO 9001 certification?
The purpose of ISO 9001 certification is to provide a framework for organizations to consistently provide products and services that meet customer and regulatory requirements, while also enhancing customer satisfaction through continuous improvement.
How long does it take to get ISO 9001 certified?
The timeline varies depending on the size and complexity of the organization, but it typically takes anywhere from 6 to 18 months.
How much does ISO 9001 certification cost?
Costs depend on factors like company size, the complexity of processes, and the chosen certification body. Expenses include implementation support, employee training, and auditing fees.
Is ISO 9001 mandatory for all businesses?
No, ISO 9001 is a voluntary standard. However, it is often a customer or contractual requirement in many industries.
How often does ISO 9001 need to be renewed?
Your ISO 9001 certificate is valid for three years. During this period, you will undergo annual surveillance audits. A full recertification audit is required every three years to renew the certificate.
What are the key components of a Quality Management System (QMS)?
A QMS typically includes the organization's quality policy and objectives, quality manual, procedures, work instructions, and records. It is structured around the organization's processes and focused on meeting customer requirements.
What's the difference between ISO 9000 and ISO 9001?
ISO 9000 is a family of quality management standards, while ISO 9001 is the specific standard within that family that contains the requirements an organization must meet to become certified.
Build a Resilient, Customer-Centric Future
Embracing ISO 9001 is more than a compliance exercise; it is a strategic investment in your organization's future. By building a robust Quality Management System, you create a foundation for resilience, continuous improvement, and sustainable growth. You empower your employees, delight your customers, and establish a culture of excellence that sets you apart from the competition.
Ready to begin your quality management journey? Explore our ISO 9001 certification services to see how we can help you achieve your goals.
Comments
ztjPEcZHr
ypiPkzTPSa
nYaLLNxyEhTFsDTVaZtE
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Advantages of ISO Certification for Businesses in Bangladesh
Discover the key benefits of ISO certification in Bangladesh, including quality assurance, cost reduction, market growth, and improved business efficiency.
LATEST POSTS

Sep 19, 2025



